Advanced Customization Options
This page is intended for advanced users with a basic understanding of HTML/CSS/JSON. Advanced configuration can greatly improve adaptability, but it's also easier to write "seemingly correct but ineffective" configurations. It is recommended to back up your data before editing.
Before You Begin
- Entry point is in Developer Settings.
- Back up your User Config / User Rules before editing to prevent configuration from being ignored due to format errors.
- For built-in final configuration, refer to "Click to expand the final config" (fields, default values, available services).
Entry Points & Priority
Common entry points (Developer Settings):
- Edit Full User Config: Edit the full config (includes
rules, translation services, styles, etc.). - Edit User Rules: Only edit the
rulesarray (this entry only accepts an array, do NOT wrap it as{ "rules": [...] }). - Injected CSS: Inject global CSS.
Priority (from high to low): Matched rules > generalRule > built-in default config.
When a rule is matched, generalRule and the matched rule will be merged, with the rule fields taking priority.
Quick Start (Common Use Cases)
1) Only translate the main content of a website
{
"rules": [
{
"matches": ["example.com"],
"selectors": ["article", ".post-content"],
"excludeSelectors": ["nav", "footer", ".comment"]
}
]
}
2) Always translate / Never translate
{
"translationUrlPattern": {
"matches": ["stackoverflow.com"],
"excludeMatches": ["www.google.com/mail/*"]
}
}
3) Use different translation services for different sites
{
"translationService": "google",
"translationServices": {
"deepl": {
"matches": ["sci-hub.se"]
}
}
}
4) Translation style differs by site
{
"translationTheme": "none",
"translationThemePatterns": {
"underline": {
"matches": ["discord.com"]
}
}
}
5) Translation causes style issues, fix via styles
{
"rules": [
{
"matches": ["youtube.com"],
"globalStyles": {
"#video-title": "max-height:unset;"
}
}
]
}
6) Do not show unconfigured translation services in popup
{
"showUnconfiguredTranslationServiceInPopup": false
}
Rules & Matching
Rule Merging
generalRule: Baseline rules for all sites.rules: Site-specific rules with top priority when matched.
Most fields in generalRule can be used in rules array elements.
Common forms of matches
matches supports string or array:
- Domain:
example.com - Full URL:
https://example.com/path/ - Wildcard:
https://*/*q=* - Match all:
*/*://*/*://*/* - Local files:
file://*
Note: *.twitter.com only matches subdomains, NOT the root domain twitter.com.
selectors / excludeSelectors
selectors: Only translate elements matched (will overwrite default range).excludeSelectors: Exclude elements from translation.
If you only want to add/remove on top of the default range, please use .add / .remove (see next section).
Inheritance & Incremental Modification (.add / .remove)
Array/Object fields support .add / .remove for incremental modification.
It is recommended to use them to avoid overwriting default rules:
[
{
"id": "twitter",
"selectors.add": ["[data-testid='tweetText'] a"],
"excludeSelectors.add": ["header"]
}
]
Common Fields Quick Reference (Partial)
Matching:
matches/excludeMatchesselectorMatches/excludeSelectorMatches
Translation range:
selectors/excludeSelectors/excludeTagsstayOriginalSelectors/stayOriginalTagsextraInlineSelectors/extraBlockSelectors
Style & layout:
translationClasses: Add extra class(es) to translationglobalStyles/globalAttributesinjectedCss/additionalInjectedCsswrapperPrefix/wrapperSuffixblockMinTextCount/blockMinWordCount
Timing & mobile:
urlChangeDelay/observeUrlChangeisShowUserscriptPagePopup
GPT-like Streaming Message Translation
{
"matches": ["chat.openai.com"],
"excludeSelectors": [".markdown *"],
"aiRule": {
"streamingSelector": ".result-streaming.markdown",
"messageWrapperSelector": ".markdown",
"streamingChange": true
}
}
See "Appendix: Rule Field Reference" at the end for more field explanations.
matches Matching Logic (Brief Explanation)
- Pure domain (no
*and no path): Compare hostname only. - Full URL (no
*): Compare protocol + host + port + path. - Contains
*or protocol omitted: Matches via wildcard (default supports http/https/file).
Examples:
twitter.com✅ Matcheshttps://twitter.com/home*.twitter.com✅ Matcheshttps://mobile.twitter.com, ❌ Does NOT matchhttps://twitter.comhttps://twitter.com/homeOnly matches the exact URLtwitter.com/*Matches all paths undertwitter.com
Site Adaptation Example (Twitter)
Below is a sample of the built-in Twitter rule, demonstrating typical use of selectors / excludeSelectors / globalStyles:
[
{
"id": "twitter",
"matches": [
"twitter.com",
"mobile.twitter.com",
"tweetdeck.twitter.com",
"pro.twitter.com",
"https://platform.twitter.com/embed*"
],
"selectors": [
"[data-testid=\"tweetText\"]",
".tweet-text",
".js-quoted-tweet-text",
"[data-testid='card.layoutSmall.detail'] > div:nth-child(2)",
"[data-testid='developerBuiltCardContainer'] > div:nth-child(2)",
"[data-testid='card.layoutLarge.detail'] > div:nth-child(2)",
"[data-testid='cellInnerDiv'] div[data-testid='UserCell'] > div> div:nth-child(2)",
"[data-testid='UserDescription']",
"[data-testid='HoverCard'] div[dir=auto]",
"[data-testid='HoverCard'] span[dir=auto]",
"[data-testid='HoverCard'] [role='dialog'] div[dir=ltr]",
"[data-testid='birdwatch-pivot'] div[dir=ltr]"
],
"excludeSelectors": [
"[aria-describedby][role=button]",
"header",
"[data-testid='radioGroupplayback_rate'] div",
"[data-testid='userFollowIndicator']",
"[class='css-901oao r-14j79pv r-37j5jr r-n6v787 r-16dba41 r-1cwl3u0 r-bcqeeo r-qvutc0']",
"[class='css-175oi2r r-1wbh5a2 r-dnmrzs']"
],
"globalStyles": {
"[data-testid='card.layoutLarge.detail'] > div:nth-child(2)": "-webkit-line-clamp: unset;",
"[data-testid='card.layoutSmall.detail'] > div:nth-child(2)": "-webkit-line-clamp: unset;",
"[data-testid='tweetText']": "-webkit-line-clamp: unset;"
}
}
]
selectors: Only translates core tweet content, avoids translating usernames/buttons.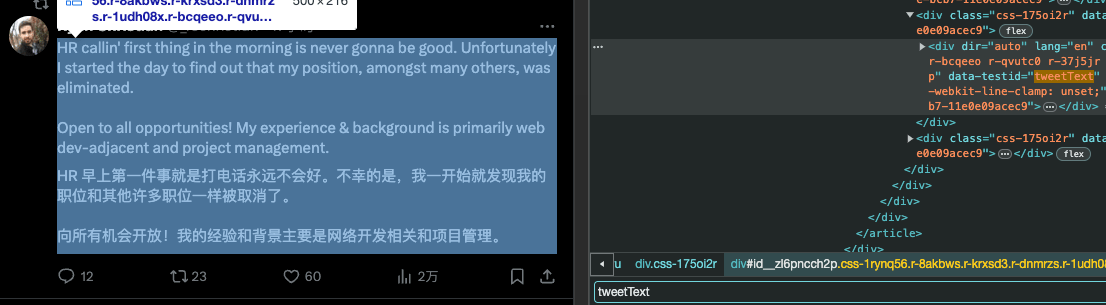
excludeSelectors: Exclude buttons, navigation, and other interactive elements.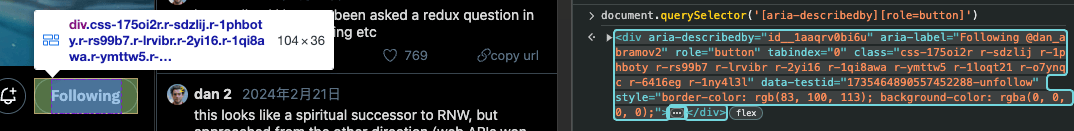
globalStyles: Remove line limit to prevent translated content from being truncated.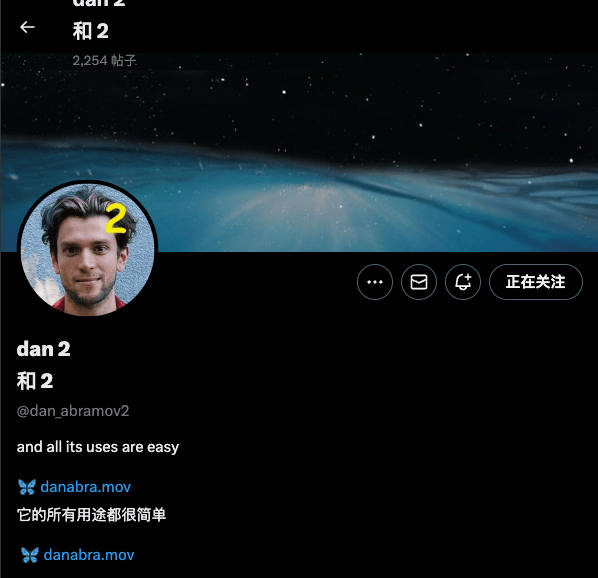
Custom Site Adaptation
You can reuse built-in rules via id, and incrementally modify using .add/.remove:
[
{
"id": "twitter",
"selectors.remove": ["[data-testid=\"tweetText\"]"],
"selectors.add": ["[data-testid=\"tweetText\"] a"],
"excludeSelectors.add": ["header"],
"excludeSelectors.remove": []
}
]
Explanation:
idcan inherit built-in rules to avoid duplicatingmatches..add/.removeis recommended for updating array fields incrementally.
Common built-in ids (partial):
isEbook: epub reader pagesisEbookBuilder: generate epub bilingual book pagespdf: PDF bilingual pages
Full built-in rules:
https://github.com/immersive-translate/next-immersive-translate/blob/main/docs/buildin_config.json
Translation Service Configuration
translationService: Default translation engine.translationServices: Service configuration and site overrides.showUnconfiguredTranslationServiceInPopup: Hide unconfigured services.
Example (Tencent):
{
"translationService": "tencent",
"translationServices": {
"tencent": {
"secretId": "xxx",
"secretKey": "xxx",
"matches": ["twitter.com"],
"limit": 3,
"maxTextGroupLengthPerRequest": 25,
"maxTextLengthPerRequest": 1800,
"apiUrl": ""
}
}
}
Explanation:
matchesspecifies which sites use this service.limitis rate limiting (requests per second).maxTextGroupLengthPerRequest/maxTextLengthPerRequestcontrol each request's size.apiUrlallows custom service endpoints.
Request Timeout Setting (Max Request Duration)
You can set request timeout per service (in ms). If using a Pro service, you can set proRequestTimeout separately.
{
"translationServices": {
"openai": {
"requestTimeout": 60000
},
"gemini": {
"proRequestTimeout": 90000
}
}
}
Tips:
- Too long timeout may lead to long waits; too short may cause frequent timeouts.
- Default value varies by service; see the final config.
proRequestTimeoutis only effective whenproviderispro(e.g., premium translation services).
Language & Translation Strategy
Always Translate / Never Translate Languages
{
"translationLanguagePattern": {
"matches": ["en"],
"excludeMatches": ["zh"]
}
}
Specify Source Language for Certain Sites
{
"sourceLanguageUrlPattern": {
"en": {
"matches": ["*.google.com"]
}
}
}
Other Common Global Configurations
Allow Rendering HTML Tags
Enable to allow translated content to retain and render HTML tags:
{
"enableRenderHtmlTag": true
}
Translation Styles & Themes
Supported values for translationTheme (subject to final config):
none, grey, dashed, dashedBorder, solidBorder, dotted, underline, mask, opacity,
paper, dividingLine, highlight, marker, marker2, blockquote, weakening, italic,
bold, thinDashed, nativeDotted, wavy, nativeDashed, nativeUnderline, background
Set style per site:
{
"translationThemePatterns": {
"highlight": {
"matches": ["discord.com"]
}
}
}
AI / Advanced Service Parameters
temperature
{
"translationServices": {
"openai": {
"temperature": 0.2
}
}
}
Custom Request Header and Body
{
"translationServices": {
"claude": {
"headerConfigs": {
"anthropic-version": "2023-06-01",
"anthropic-dangerous-direct-browser-access": "true"
},
"bodyConfigs": {
"max_tokens": 2048
}
}
}
}
How to Customize for Gemini Models
Gemini models have built-in defaults. To override them, use modelsOverrides:
{
"translationServices": {
"gemini": {
"modelsOverrides": [
{
"models": ["gemini-2.5-flash", "gemini-2.5-flash-lite"],
"bodyConfigs": {
"temperature": 0.1
}
}
]
}
}
}
Tip: modelsOverrides also works for other AI services; it overrides configs on model name match.
Strictly Follow Custom Prompts
To reduce "hallucinations" by LLMs, the extension has a translation quality validation. It checks the token ratio between response and request text as a translation correctness check. If the ratio is abnormal (too high or too low), the result is considered invalid and the next service is attempted. If your custom prompt is for non-translation tasks (e.g., rewriting, polishing, or instruction), the token ratio may not meet the expected standard. You can enable strictPrompt mode to skip the ratio check.
{
"translationServices": {
"claude": {
"strictPrompt": true
}
}
}
Custom Multilingual Prompts (Example)
{
"translationServices": {
"openai": {
"langOverrides": [
{
"id": "auto2ja",
"systemPrompt": "あなたはプロの翻訳エンジンです。",
"prompt": "次のテキストを{{to}}に翻訳してください:\n\n<text>\n{{text}}\n</text>",
"multiplePrompt": "<yaml>\n{{yaml}}\n</yaml>",
"subtitlePrompt": "<yaml_subtitles>\n{{yaml}}\n</yaml_subtitles>"
}
]
}
}
}
Terminology & Machine Translation
Latest AI Terminology feature is supported, only effective for AI services.
Machine translation does not use terminology by default (machine translation typically uses placeholders, which can lower quality). To force enable (not recommended):
{
"enableMachineTranslateTerms": true
}
Cache Cleaning Cycle
The extension cleans translation cache automatically every 30 days to avoid performance issues from excessive cache.
{
"cacheMaxAgeDay": 30
}
Injected CSS vs. globalStyles
- Injected CSS: Global CSS injection, good for site-wide fixes.
- globalStyles: Rule-level style override, good for site-specific fixes.
Injected CSS example:
.immersive-translate-target-wrapper img {
width: 16px;
height: 16px;
}
Troubleshooting & Common Pitfalls
*.twitter.comdoes NOT include the root domain; includetwitter.comseparately.selectorswill overwrite default translation range; prefer.add/.removewhen possible.- A
matchespattern likeexample.com/pathwill be evaluated as a wildcard pattern. Make sure if you need full URL matching. - If configuration is ineffective: first check the final merged config, then refresh the page.
- A trailing comma in JSON will cause the config to be ignored.
Appendix: Rule Field Reference
This is a reference for Rule fields (document version), covering common fields. For full/latest fields, check the final config.
Tip: For array/object fields, you may use .add / .remove for incremental modifications to avoid overwriting defaults.
export interface Rule {
// Website matching
id?: string; // Built-in Rule ID, use to reuse built-in rules
matches?: string | string[]; // Only match these sites
excludeMatches?: string | string[]; // Exclude specific sites
selectorMatches?: string | string[]; // Match by selector instead of URL
excludeSelectorMatches?: string | string[]; // Exclude by selector, same as above
// Translation range
selectors?: string | string[]; // Only translate matched elements
excludeSelectors?: string | string[]; // Excluded elements will NOT be translated
excludeTags?: string | string[]; // Excluded tag names will NOT be translated
// Additional translation range (if not effective, use selectors.add / selectors.remove)
additionalSelectors?: string | string[]; // Additional translation range
additionalExcludeSelectors?: string | string[]; // Additional excluded elements
additionalExcludeTags?: string | string[]; // Additional excluded tags (may be deprecated in some versions)
// Keep original
stayOriginalSelectors?: string | string[]; // Matched elements remain unchanged
stayOriginalTags?: string | string[]; // Matched tags remain unchanged (e.g., code)
// Block or Inline
extraBlockSelectors?: string | string[]; // Treat matched elements as block
extraInlineSelectors?: string | string[]; // Treat matched elements as inline
inlineTags?: string | string[]; // Treat matched tags as inline
preWhitespaceDetectedTags?: string | string[]; // Auto line break for matched tags
// Translation style
translationClasses?: string | string[]; // Add extra class(es) to translated content
// Global styles
globalStyles?: Record<string, string>; // Modify page styles
globalAttributes?: Record<string, Record<string, string | null>>; // Modify element attributes
// Injected styles
injectedCss?: string | string[]; // Embedded CSS
additionalInjectedCss?: string | string[]; // Additional CSS to inject
// Context
wrapperPrefix?: string; // Prefix for translation container
wrapperSuffix?: string; // Suffix for translation container
// Line break configuration for translation
blockMinTextCount?: number; // Minimum character count to treat as block
blockMinWordCount?: number; // Minimum word count to treat as block
// Minimum content length to allow translation
containerMinTextCount?: number; // Minimum chars for the element to be recognized
paragraphMinTextCount?: number; // Minimum chars for a paragraph
paragraphMinWordCount?: number; // Minimum words for a paragraph
// Line-breaking for long paragraphs
lineBreakMaxTextCount?: number; // Max chars per line for forced breaking
// When to trigger translation
urlChangeDelay?: number; // Delay translation after entering page
observeUrlChange?: boolean; // Retranslate when URL changes
// Mobile
isShowUserscriptPagePopup?: boolean; // Show page popup on mobile
fingerCountToToggleTranslagePageWhenTouching?: number; // Deprecated
// AI streaming translation
aiRule?: {
streamingSelector: string; // Selector for elements being translated
messageWrapperSelector: string; // Selector for message content
streamingChange: boolean; // Whether it's real-time incremental update
};
}